Cattley Guava
Psidium cattleyanum
Eucalyptus-Like family (Myrtaceae)
Post-Cook introduction
Small tree or shrub planted for its round or elliptical dark reddish purple or yellow edible and widely naturalized and forming thickets in lowland areas. Becoming 20–50 ft (6–15 ) high, with slightly angled trunk 4–12 inches (0.1–0.3 ) in diameter. Bark gray or light brown, smooth, peeling off and exposing light greenish brown inner layers. Inner bark is light pink, bitter and astringent. Twigs brown, hairless.

©2012. Forest And Kim Starr
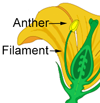
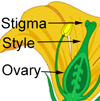
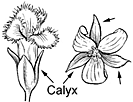
Flowers 1–2 on short stalks at leaf bases, white, less than 1 inch (2.5 ) across, composed of greenish conical base () less than 1⁄4 inch (6 ) long, 4–5 rounded green that remain at top of 4–5 elliptical white petals, many threadlike white and with inferior and slender
(berries) 1–2 on slender stalks at leaf bases or back of leaves, round or elliptical, 1–1 1⁄2 inches (2.5–4 ) long, dark reddish purple or sometimes yellow, with 4 rounded thick 1⁄4 inch (6 ) long at thick-walled, pinkish or whitish, juicy, slightly sour to sweet edible pulp, aromatic. Seeds are many, rounded or elliptical, 3⁄16 inch (5 ) long, hard, light brown or yellow.
Sapwood is yellowish white and heartwood pale reddish brown. A fine-textured, moderately heavy wood used only for fuelwood in Hawaii.
are eaten raw or made into jam or jelly with strawberry flavor. One variety of larger size with large yellow is called yellow strawberry guava.
Introduced into Hawaii in 1825 for the edible but now thoroughly naturalized and established. It forms thickets in moist lowland areas up to about 2500 ft (762 ) elevation, rarely to 4,000 ft (1,220 ). Classed as a weed in pastures, rangelands, and waste places. Grown also in southern California and Florida.
Special areas
Waimea Arboretum, Wahiawa, Tantalus, Aiea, Kalopa, Pepeekeo
Range
Native of Brazil
Other common names
purple strawberry guava, Cattley guava, waiawi
Botanical
Psidium cattleianum Sabine, Psidium littorale Raddi