Pāpala Kēpau
Ceodes brunoniana
Verbena/Four-O'Clock family (Nyctaginaceae)
Native species ()
Small native tree of dry forests, with paired elliptical leaves, very large open flower clusters with many small flowers on long slender widely forking stalks, and narrow sticky To about 18 ft (5.5 ) and 4 inches (110 ) in trunk diameter. Bark light gray or light brown, smoothish; inner bark whitish, slightly bitter. Twigs green to brown. Young twigs and leaves with tiny pressed brown hairs.

©2012 Eric White
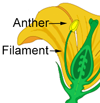
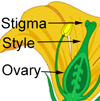
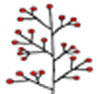
Flower clusters () very large and open or loose, 6–12 inches (15–30 ) long and broad. Flowers many, small, on many long slender widely forking stalks, 3⁄8 inch (10 ) long, composed of greenish tubular or narrowly funnel-shaped finely hairy with five short, pinkish 8–12 attached inside tube and extending beyond, and with narrow long and dot
(anthocarp) narrowly cylindrical, consisting of enlarged 3⁄4–1 3⁄8 inches (20–35 ) long and 1⁄8 inch (3 ) in diameter, widest at middle, spreading at five-ridged, sticky and exuding glue, enclosing the narrow one-seeded () with at
Wood is whitish yellow, very lightweight, very soft, and brittle. It “honeycombs” in air drying and is not used.
Widespread in dry forests and at edges of lava fields, mostly at 2000–4000 ft (610–1219 ) altitude.
Special areas
Wahiawa, Volcanoes
Champion
Height 50 ft (15.2 ), c.b.h. 6.3 ft (1.9 ), spread 31 ft (9.4 ). Hoomau Ranch, Honomalino, Hawaii (1968).
Range
Oahu, Lanai, Maui, Hawaii only
Botanical
Pisonia brunoniana Endl., Heimerliodendron brunoianum (Endl.) Skottsb., Pisonia inermis G. Forst., not Jacq.
The Hawaiian common name pāpala kēpau is from kepau, the name for tar, pitch, etc. A sticky liquid or glue exudes from the and catches insects. Hawaiians formerly used the viscous as birdlime to catch small birds.